<Philosophy & Policy>
Environmental Policy (ISO 14001)
“We recognize that protecting the irreplaceable global environment is a shared and vital responsibility of all humanity, and we are committed to reducing our environmental impact.”
To embody this fundamental philosophy, we faithfully implement the following initiatives:
1.We conduct appropriate environmental management activities to reduce the environmental impact of our group’s operations, products, and services, thereby contributing to the development of a sustainable society.
2.We utilize our Environmental Management System effectively to prevent pollution and promote continuous improvement.
3.We comply with environmental laws and regulations, as well as other requirements to which the TBK Group agrees.
4.We work to suppress greenhouse gas emissions throughout all business activities and across the entire lifecycle of our products and services.
5.Based on our core philosophy, we set environmental objectives and targets, formulate implementation plans, and carry out concrete actions—especially focusing on the following
(1)Promotion of energy and resource conservation
(2)Reduction and reuse of waste
(3)Reduction of environmental impact from products
6.We promote environmental education and awareness activities to raise the environmental consciousness of every employee and contribute to the local community.
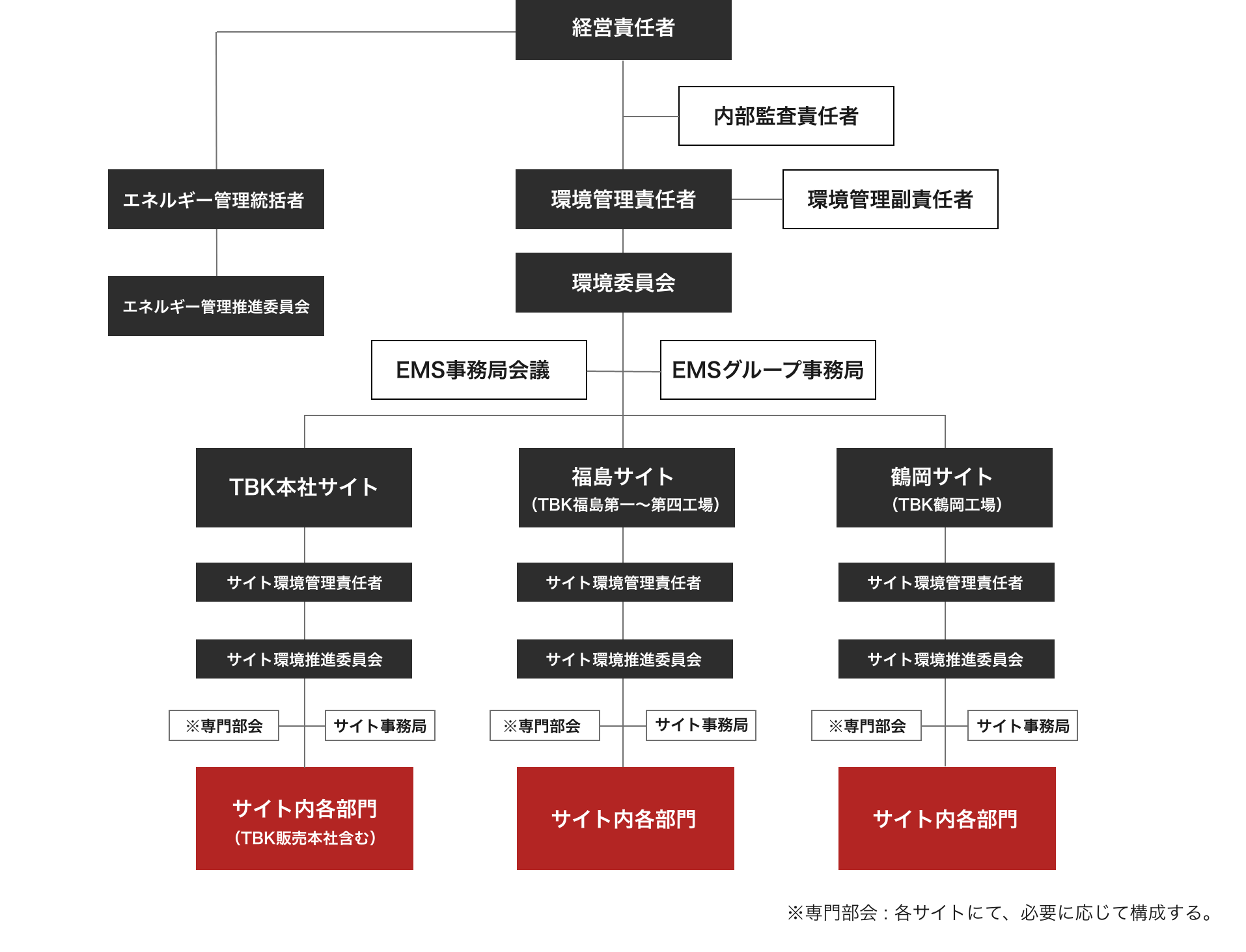
<Framework> To appropriately manage environmental issues across the TBK Group, we have appointed Environmental Management Officers under the supervision of the President, and we promote group-wide environmental activities.
| Category | Material Issue | Key Indicator(KPI) | FY2024 Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment(E) | Contribution to society and the environment through business activities | Total CO₂ emissions | ▲15% compared to FY2013 |
| Development of eco-friendly products (lightweighting, electrification) | Weight reduction in brakes | ▲15% reduction in brake weight |
Our group recognizes climate change as one of the most critical challenges in both society and business, and we are actively addressing this issue. In the following, we present information regarding the four areas recommended for disclosure by the TCFD—“Governance,” “Strategy,” “Risk Management,” and “Metrics and Targets”—as well as provide data on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
1.Governance
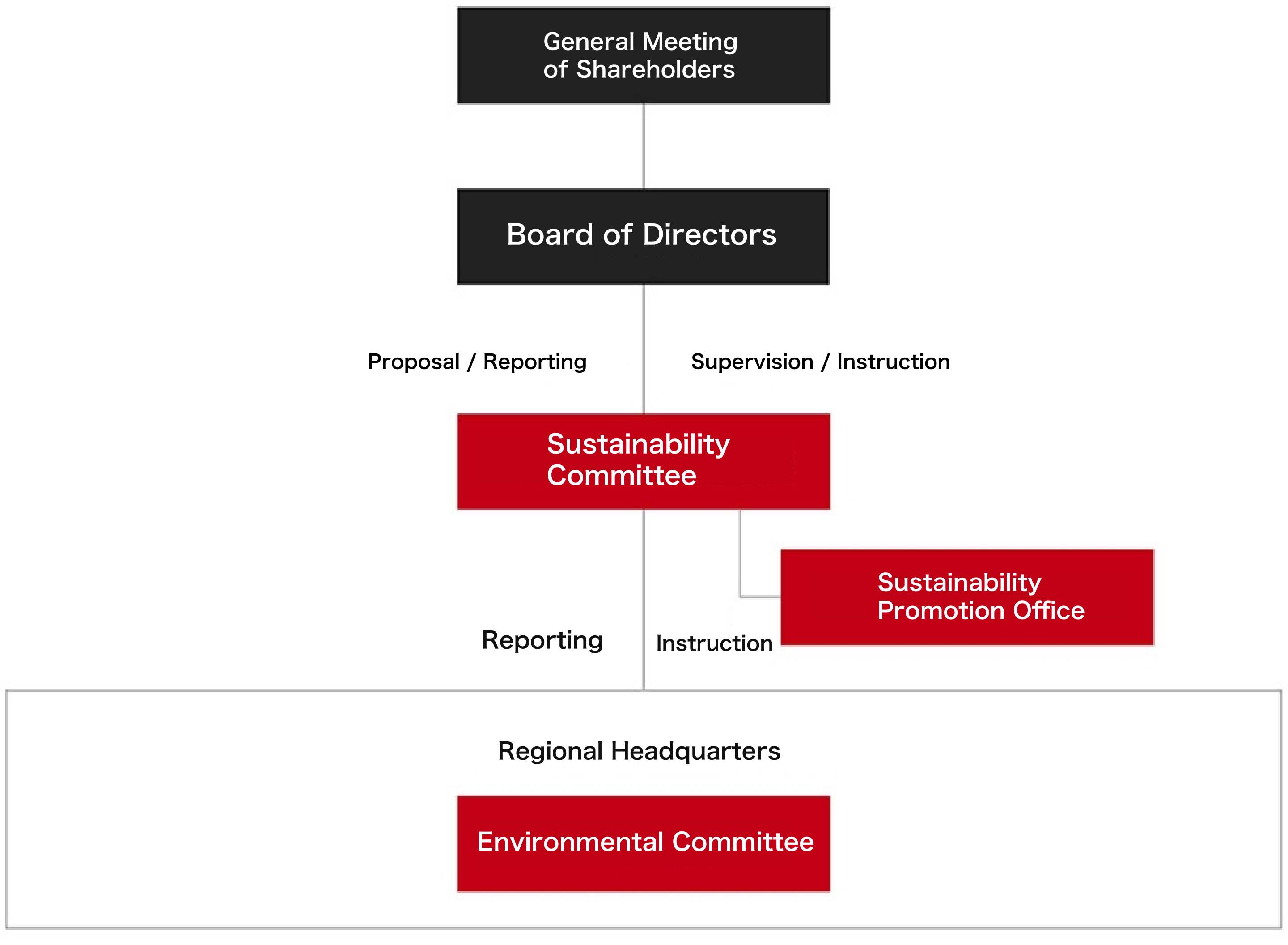
To strengthen the formulation and promotion structure of company-wide sustainability efforts and strategic initiatives, the Sustainability Committee was established on July 1, 2022.
The Sustainability Committee is chaired by the President & CEO, and its members primarily consist of senior management, including regional heads, functional leaders, subsidiary presidents, and department heads.
Important risks related to climate change are reported and proposed to the Board of Directors as appropriate, in line with the company's overall risk management process.
Specific analyses and initiatives related to climate change are carried out under the supervision of the Sustainability Committee. In addition, Environmental Committees at each site coordinate with group companies to promote countermeasures and manage targets related to climate change. These activities are reported to and reviewed by the Sustainability Committee.
Sustainability Promotion Framework
The TBK Group has conducted a qualitative scenario analysis to assess the potential impact of climate change on its business and performance.
Recognizing the importance of preparing for a variety of possible future developments, we referred to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) to conduct our analysis using both a “Below 2°C scenario” and a “4°C scenario.”
(Transition to a Low-Carbon Economy)
(Heightened Physical Climate Risks)
We consider both "transition risks and opportunities"—arising from changes in society due to policies, technologies, and market shifts—and "physical risks and opportunities"—arising from natural disasters, rising temperatures, and other environmental changes.
The climate-related risks and opportunities identified by the TBK Group, along with our current response measures, are summarized in the table below.
Below 2°C Scenario
(Transition to a Low-Carbon Economy)
A scenario in which global climate policies are advanced and a carbon-neutral society is realized. With stronger environmental regulations from international and Japanese authorities and rapid technological innovation, significant changes in society and industrial structures are expected.
| Changes in Society |
Timeframe
|
Risk | Opportunity | Response | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policies and Regulations | Introduction of carbon tax / GHG regulations | Mid-term (2030) | Increased costs proportional to GHG emissions | - | Proactive emissions reduction in anticipation of regulation |
| Technological Development | Stricter fuel efficiency for ICE vehicles | Mid-term (2030) | Risk of sales decline due to competitors’ fuel-efficient products | Expand sales of fuel-efficient products aligned with customer needs | Develop products aligned with low-emission needs |
| Electrification of commercial vehicles | Mid-term (2030) | Decline in demand for ICE-related products (e.g., water/oil pumps) | Sales growth from expanding EV product lineup | Accelerate development of EV-compatible products | |
| Market Trends | Grid parity not yet achieved | Mid-term (2030) | Higher electricity costs from use of renewable energy | - | - Install solar power at plants - Reduce electricity use through energy-efficient equipment |
| Rise in raw material prices | Mid-term (2030) | Increase in metal/resin unit costs | - | Negotiate price transfer to customers | |
| Carbon-neutral supply chain requests | Mid-term (2030) | Increased capital investment for energy-saving and renewable systems | Contribution to customers' Scope 3 CN targets expands sales opportunities | - | |
CN: Carbon Neutral
4°C Scenario
(Heightened Physical Climate Risks)
A scenario where global decarbonization efforts are insufficient, and the world faces increased physical climate risks.
| Changes in Society | Timeframe | Risk | Opportunity | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rising average temperatures (chronic) | Long-term(2050) | Lower productivity due to hotter factory environments → higher labor costs | - | Improve work environment (air conditioning, break time, etc.) |
| Intensification of extreme weather (acute) | Short-term(2025) | Damage to facilities due to frequent wind/flood disaster | - |
|
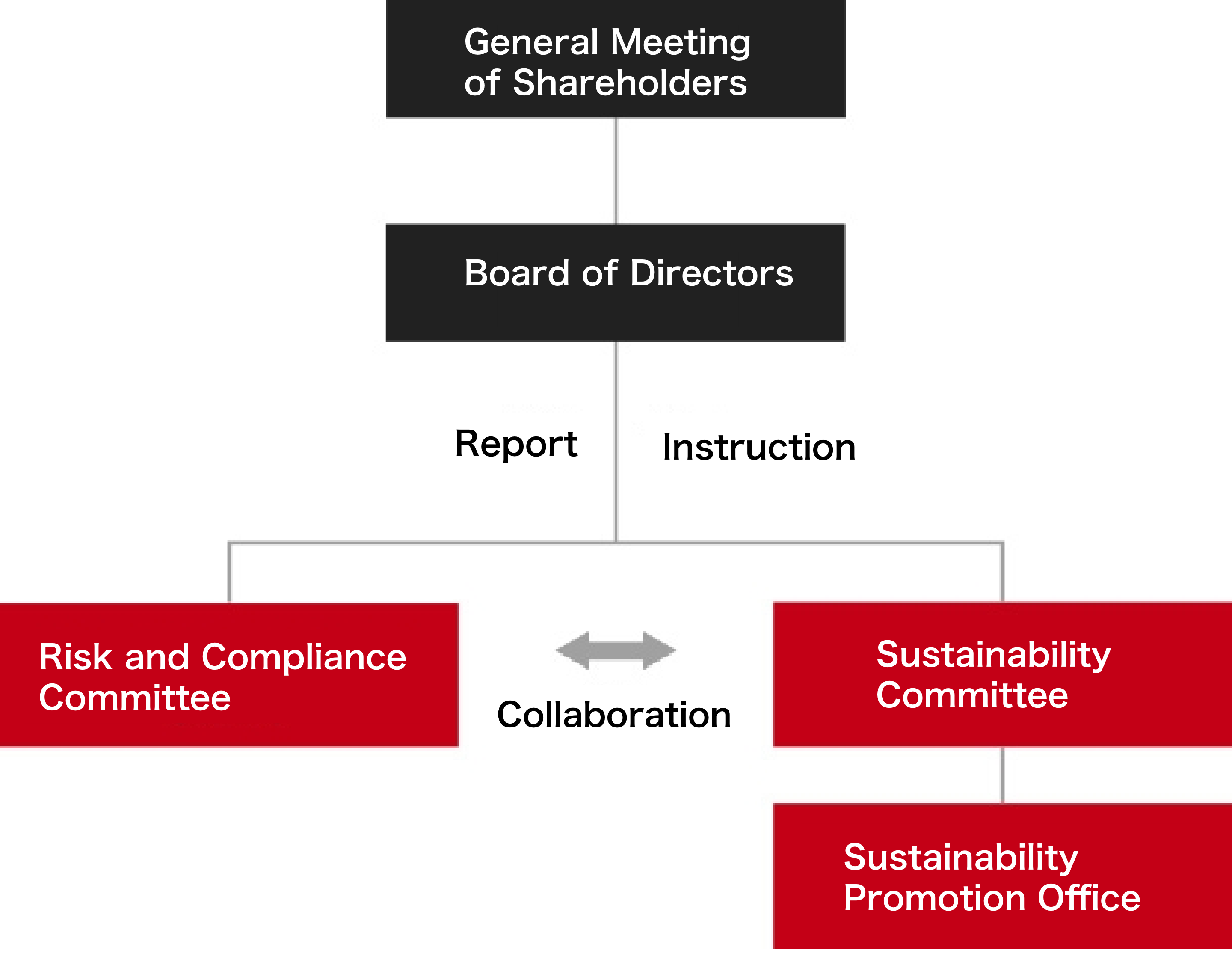
The TBK Group has established a Risk and Compliance Committee, chaired by the President & CEO, in accordance with its Risk Management and Compliance Regulations.
The committee meets quarterly to identify key risks based on risk assessments submitted by each department, taking into account impact and duration.
Reports related to risk and compliance from group companies are reviewed, and significant matters are submitted to the Board of Directors for deliberation and decision-making.
For climate-related risks, the Risk and Compliance Committee collaborates with the Sustainability Committee, and reports are made to the Board as part of our enterprise risk management process.
Climate Change Risk Management Structure
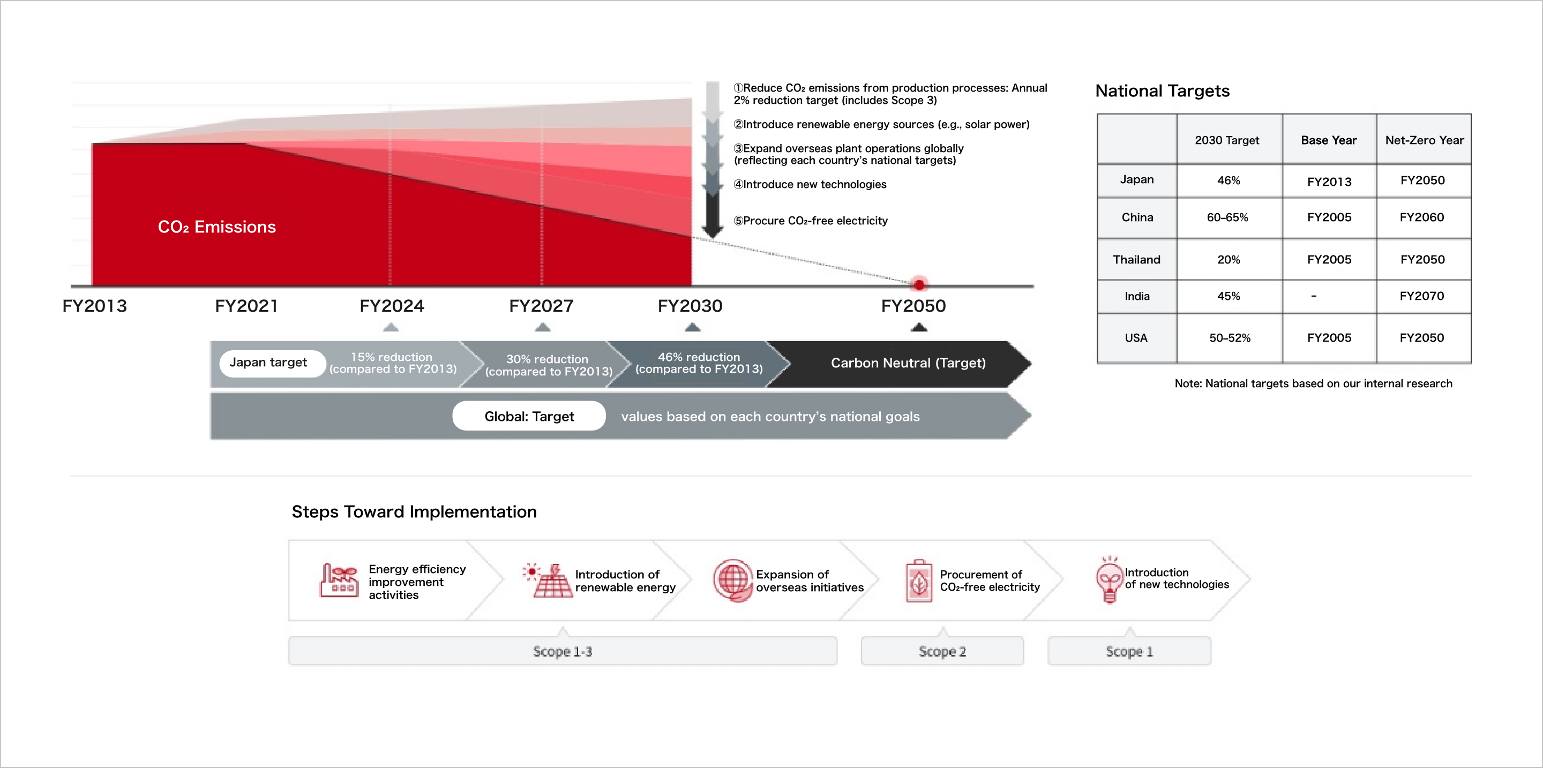
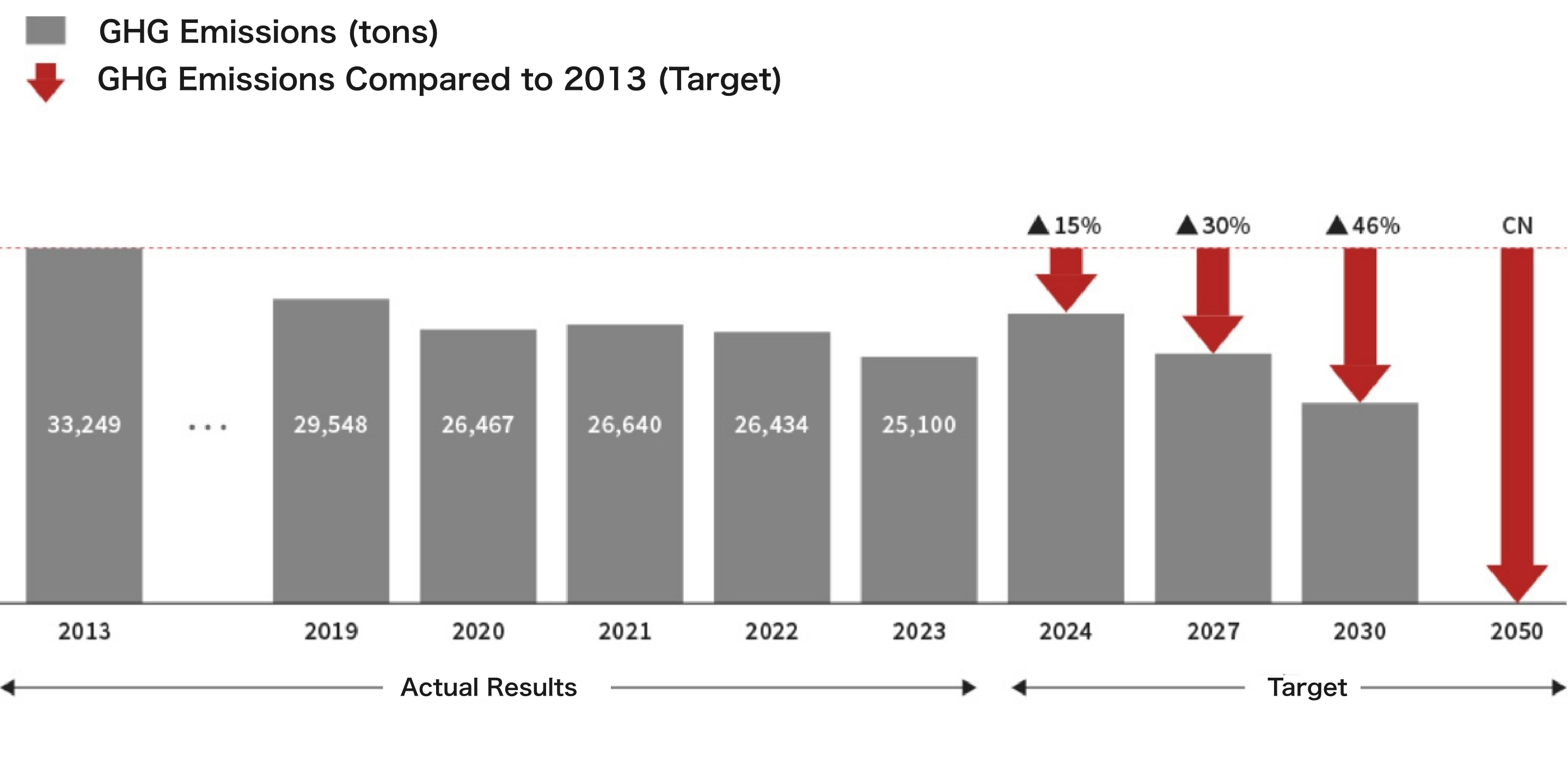
The following outlines GHG emissions from our domestic group companies.
As part of our ESG-focused strategy, TBK has set a domestic target to achieve carbon neutrality by FY2050.
We will accelerate energy-saving efforts and the use of renewable energy to achieve this goal.
For overseas subsidiaries, we are currently identifying GHG emissions and formulating Scope 1 and 2 reduction targets in accordance with each country's policy.
We are also working on measuring Scope 3 emissions and setting targets related to newly identified business opportunities.
TBK Group’s Renewable Energy Adoption and Future Outlook Solar power systems have already been installed at TBK Fukushima Plant and TBK India Private Ltd.
We also plan to install solar systems using Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) at the Fukushima No. 2 carport and the plant in Thailand.
At our headquarters, we are promoting the use of CO₂-free electricity.
The Fukushima plant is also considering switching electricity suppliers to further advance decarbonization.
TBK Group will continue to accelerate its transition to sustainable energy and strengthen efforts for environmental conservation.

Solar Power Installation at TBK India Private Ltd.
Our group promotes environmental responsibility throughout the entire product lifecycle while working closely with vehicle and engine manufacturers to reduce costs and accelerate the development process.
From the planning stage through design and development, we aim to minimize environmental impact by pursuing energy efficiency and effective use of resources.
| Category | Materiality | KPI | FY2024 Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environment(E) | Contribution to society and the environment through business activities | Development of environmentally friendly products (lightweighting and electrification) | Brake weight reduction: ▲15% |
Our group views electrification not merely as product development, but as a business opportunity encompassing entire system solutions.
Through this approach, we aim to establish a new market position as a “Tier 0.5” supplier—beyond the conventional Tier 1.
(Note: In a supply chain, Tier 1 suppliers deliver parts directly to OEMs, while Tier 2 suppliers provide components to Tier 1 suppliers, and so on.)
The Engine Assist System (Mild Hybrid System) developed by the TBK Group is an environmentally conscious product that assists engine output during vehicle or construction machinery startup and acceleration, thereby reducing engine load, improving fuel efficiency, and contributing to energy savings.
This system is currently undergoing evaluation by a construction machinery manufacturer, and a mass production project for construction equipment engines has been launched.
Trucks and buses utilize compressed air for air brakes and air suspension systems.
In conventional engine vehicles, air compressors powered by the engine supply compressed air. In electric vehicles (EVs), however, electrically driven compressors are required. Similarly, power steering oil pumps must also be electrified.
TBK, in collaboration with its Chinese joint venture Changchun FAWSN TBK, has developed an integrated unit combining an electric compressor and an electric power steering pump. This design achieves both weight reduction and space savings.

Electric Compressor Integrated with Electric Power Steering Pump
The TBK Group is developing e-Axle units for large commercial electric trucks, including Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs).
The design concept uses existing axle and suspension mounting components to minimize modifications from existing vehicles and reduce resource waste.
To support compact and highly efficient motor use, a transmission with gear-changing capabilities has been incorporated, enhancing energy efficiency.
Vehicle performance characteristics and transmission shift timing have been optimized through actual vehicle testing at the Tokachi Proving Ground, ensuring maximum performance with minimum energy input.
These initiatives contribute to the reduction of CO₂ emissions.
(Note: An e-Axle is an electric drive module that integrates an EV motor, reduction gear, and associated components.)

e-Axle Under Development for Heavy-Duty Trucks

On-Vehicle Testing at the Tokachi Proving Ground Test Course
TBK Sales Co., Ltd. manufactures and sells rebuilt expanders as genuine replacement parts for vehicle manufacturers.
These environmentally friendly products ensure quality equivalent to that of new parts while reusing over 85% of components by weight, making them a sustainable choice for the planet.
Rebuilt Expander
TBR Co., Ltd. (now TBK Tsuruoka Plant) has achieved product weight reduction by applying thinner wall designs compared to conventional specifications.
By developing a prototype mold for electronic component covers (Note 1) and utilizing ultra-high-speed die casting technology (Note 2), the company successfully produced castings with significantly reduced weight.
This initiative enables thinning in areas where mechanical strength is not required, achieving both weight reduction and lower environmental impact.
Note 1: A mold used for prototyping electronic components and verifying lightweight designs.
Note 2: A manufacturing technique that enables high-precision and rapid casting, ideal for producing complex shapes and thin-walled parts.

Lightweight Product

Wall Thickness Reduct
The TBK Group places a strong focus on waste reduction and the effective use of resources in accordance with its environmental policy.
To minimize waste generated during the production process, we actively implement the 3Rs — Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle — with the goal of lowering environmental impact and promoting efficient resource utilization.
In addition, chemical substance management is conducted in compliance with domestic and international regulations, also guided by our environmental policy. We are committed to both pollution prevention and continuous improvement.
Waste emissions: 1% reduction compared to the previous fiscal year
(Target scope: 3 domestic group companies)
The TBK Group actively promotes the reduction and recycling of waste generated during the casting process.
At our casting plants, we have introduced a process to solidify waste molten iron ("discarded melt") into ingots (Note 1), significantly reducing the volume of waste sand (Note 2) that was previously generated in large quantities.
This approach enables both waste reduction and resource reuse, thereby lowering environmental impact.
Slag Recycling at Kimura Katanyu Co., Ltd.
At Kimura Katanyu Co., Ltd., we have also implemented a recycling initiative targeting slag generated during casting.
Since 2020, the company has been recycling this slag for use as roadbed material.
As of today, 100% of slag produced is recycled, significantly contributing to the overall waste reduction efforts across the TBK Group.
1. Ingot formation is the process of melting metal and solidifying it into block form.
2. Waste sand is a byproduct generated after use in the casting process.

Pouring Waste Molten Iron into Molds for Ingot Production

Solidified Iron Formed into Ingots
The iron has solidified and been formed into ingots.
At TBR Co., Ltd. (now TBK Tsuruoka Plant), the holding temperature of aluminum melting furnaces was previously maintained using LPG burners.
By installing electric heaters near the tapping outlet, the company successfully reduced the usage of LPG—a fuel with a high CO₂ emission factor.
This initiative has led to a significant reduction in CO₂ emissions, improved energy efficiency, and lowered operating costs.
The TBK Group will continue to advance such initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality.

Electric Heater Used for Maintaining Temperature in Aluminum Holding Furnace
The TBK Group is actively promoting the disposal of obsolete molds and the recycling of iron scrap.
This initiative contributes to reducing storage space needs and results in lower energy consumption and CO₂ emissions.
We will continue these efforts to enhance both environmental protection and economic sustainability.
At TBR Co., Ltd. (now TBK Tsuruoka Plant), an oil-water separator has been installed to treat wastewater generated during cutting processes.
The device separates oil from water in used water-soluble coolants, reducing waste volume.
The separated water is then reused as dilution water for new water-soluble coolants.
Note: Water-soluble coolant is a type of coolant used in machine tools to improve lubrication, flush out chips, and cool down the heat generated between tools and workpieces during metal cutting and grinding.

Left (in clear plastic container): Separated water Center back: Oil-water separator Right (in black plastic container): Separated oil
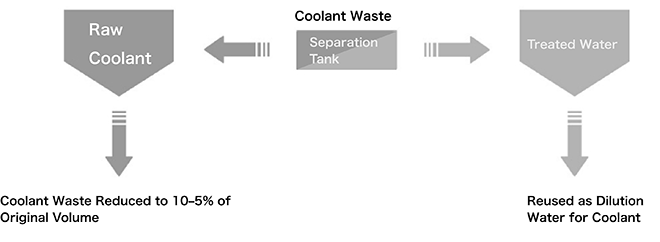
Reused as Dilution Water for Coolant
At the TBK Fukushima Plant, we are working to recycle cast iron chips—a type of industrial waste—by compressing them into briquettes, which are then reused as casti
ng materials at our group company, Kimura Katantan.
This process promotes effective resource utilization and contributes to waste reduction.
Looking ahead, we are considering expanding the equipment used for briquetting to further advance resource recycling efforts.
※ Briquetting refers to the process of compressing metal shavings or powder into reusable solid blocks (briquettes).
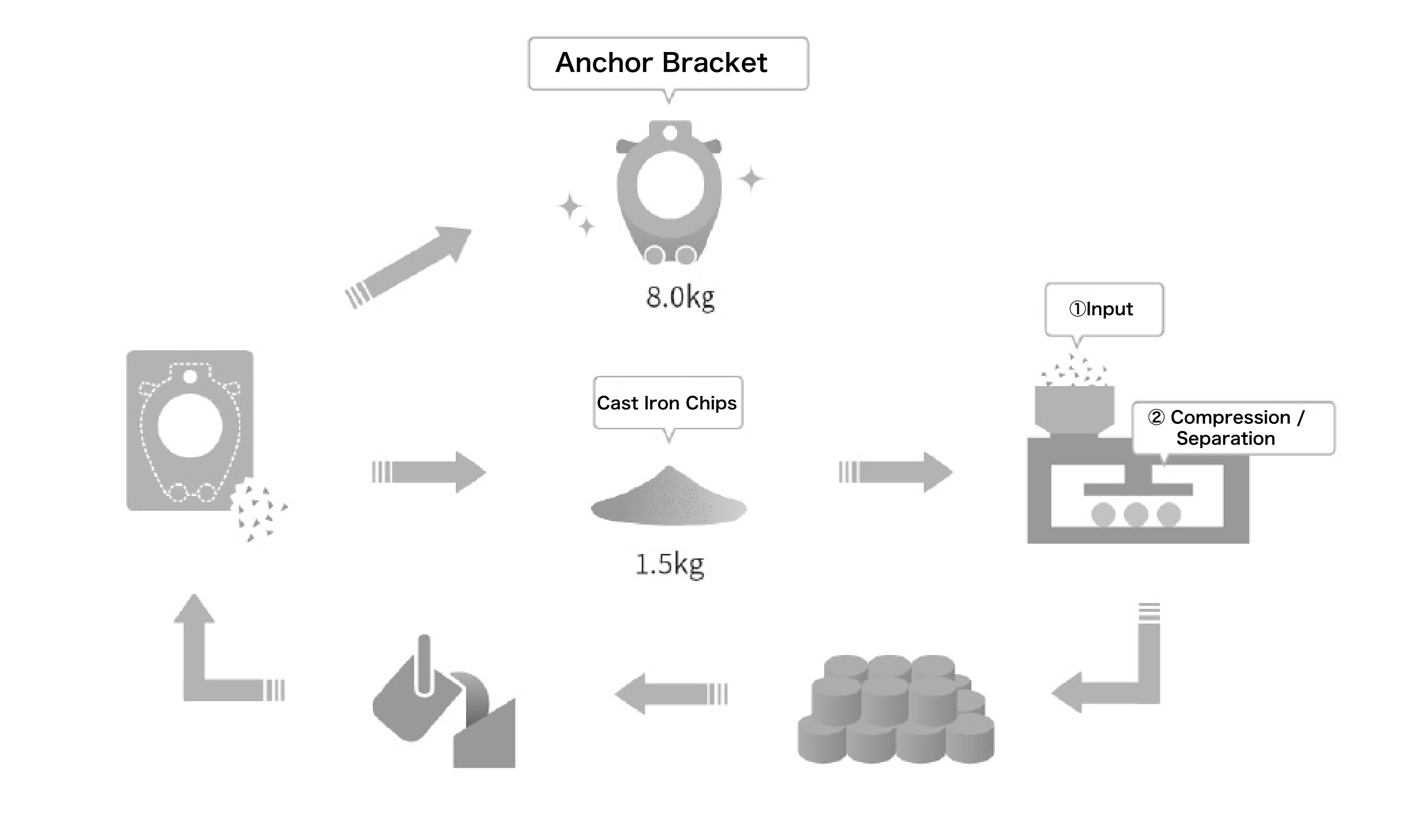
Flow from Generation to Reuse of Cast Iron Chips
Many chemical substances are already present in our everyday lives, and modern factories often handle cutting fluids and lubricants that contain new chemical compounds.
At TBR Corporation (now TBK Tsuruoka Plant), we are committed to protecting those who handle such substances and to producing safe and reliable products by promoting awareness of the importance of risk assessments.
In the training sessions, participants learn about the purpose and methods of workplace patrols and inspections, key points to observe, and are encouraged to reflect on what their ideal workplace should look like.
Additionally, individuals who have completed specialized training courses in chemical substance management are appointed as dedicated managers and are actively engaged in overseeing daily operations.

Certificate of Completion for Specialized Training in Chemical Substance Management

